Choosing a fibre from a design perspective can be challenging enough, but the fibre that a fabric is made from also has numerous environmental and social impacts. It can be difficult to work out the best option when selecting a fibre.
Introducing Fibre Focus, our fabric blog that breaks down the various impacts of a fibre from an environmental, social justice and design standpoint. It is important to also consider any potential impacts a fibre might have if it were to become more popular.
Design advantages :
- Strong and durable
- Moisture absorbent
- Temperature regulating, so warm in winter and cool in summer
- Resistant to UV light and mold
- Has affinity with most natural and synthetic dyes
Design disadvantages :
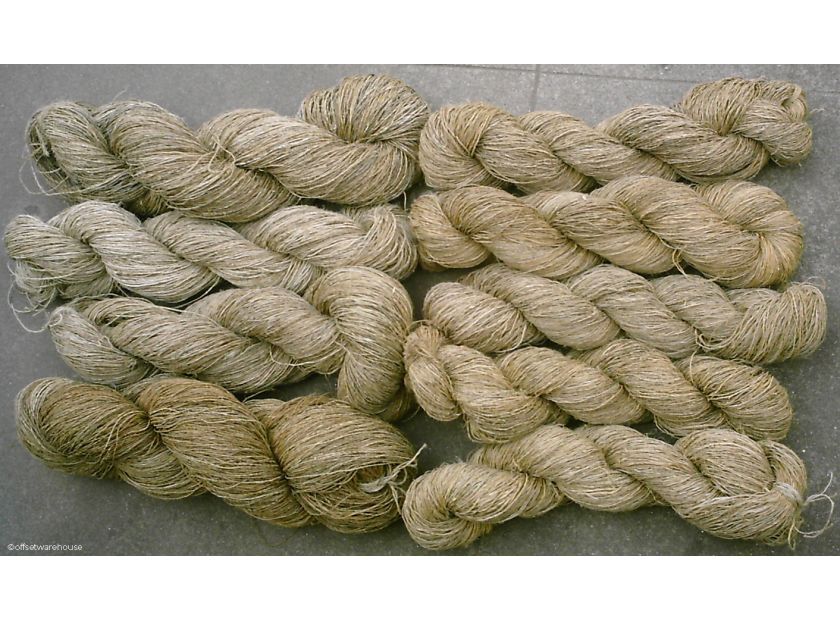
- Raw hemp can be coarse and require processing to attain the same handle as other natural fibres, such as cotton
- Hemp fabric’s coarse handles means it can require more pressing or ironing during its use
- Hemp’s fibres are darker in colour than cotton and so may require higher concentrations of dye
Environmental impacts :
- Hemp flourishes without pesticides or fertilisers and therefore it doesn’t harm the air, water or soil
- Hemp plants grow very quickly and yield a lot of usable fibre
- Hemp has hundreds of uses outside of textiles. Cultivating crops that have multiple uses is an economical use of time and resources
- Hemp leaves have a large surface area and absorb a lot of CO2 during growth
- Growing hemp requires much less water than other natural fibres
- Growing hemp does not exhaust the soil of its nutrients
- Hemp is biodegradable
- Hemp is a cellulose, natural fibre that is grown as opposed to ‘made’ in a lab
- Hemp fibres can be processed and spun by hand, this saves energy during spinning and avoids carbon emissions
- Hemp fibres are generally easy to recycle because of their strength
- Hemp plants have very long roots and help prevent soil erosion
- Hemp can grow in many places worldwide and so fossil fuels are saved during transportation
Social impacts :
- Hemp farmers work with far fewer pesticides than other fibre producers. This translates as better air, water and soil quality for local communities, as well as improved farmer health
- Consumers of hemp fabric can expect fewer residual pesticide chemicals on their textiles
- Hemp grows very quickly, so farmers can increase yields and generate more income
- Famers can also save on production cost because they buy comparatively less chemicals than other fibre farmers
- Hemp producers can generate more profits because the plant has so many uses in cosmetics, textiles, food and building materials
Positive potential impacts :
- Fewer chemical pesticides in the environment
- A decreased water footprint
- Decreased farmer dependence on large chemical companies
- Preservation of air, water and soil quality
- Research is being conducted for hemp biofuel – this could have many beneficial impacts
Negative potential impacts :
- Job loss for farmers in other fibre industries, and therefore a loss of income
- Increased use of energy during the use of hemp fabric
- Increased use of dye during fabric production
So there you have it, a simple breakdown of hemp’s impacts that you can keep in mind when buying, sourcing or designing.
Fibre Focus: Hemp









 France
France
 Germany
Germany
 Italy
Italy
 Spain
Spain
 United States
United States
 India
India











